Regression
DownloadTélécharger
Actions
Vote :
ScreenshotAperçu
Informations
Catégorie :Category: mViewer GX Creator App HP-Prime
Auteur Author: unluckyowl13
Type : Application
Page(s) : 15
Taille Size: 668.53 Ko KB
Mis en ligne Uploaded: 07/03/2018 - 05:06:28
Uploadeur Uploader: unluckyowl (Profil)
Téléchargements Downloads: 53
Visibilité Visibility: Archive publique
Shortlink : http://ti-pla.net/a1381805
Type : Application
Page(s) : 15
Taille Size: 668.53 Ko KB
Mis en ligne Uploaded: 07/03/2018 - 05:06:28
Uploadeur Uploader: unluckyowl (Profil)
Téléchargements Downloads: 53
Visibilité Visibility: Archive publique
Shortlink : http://ti-pla.net/a1381805
Description
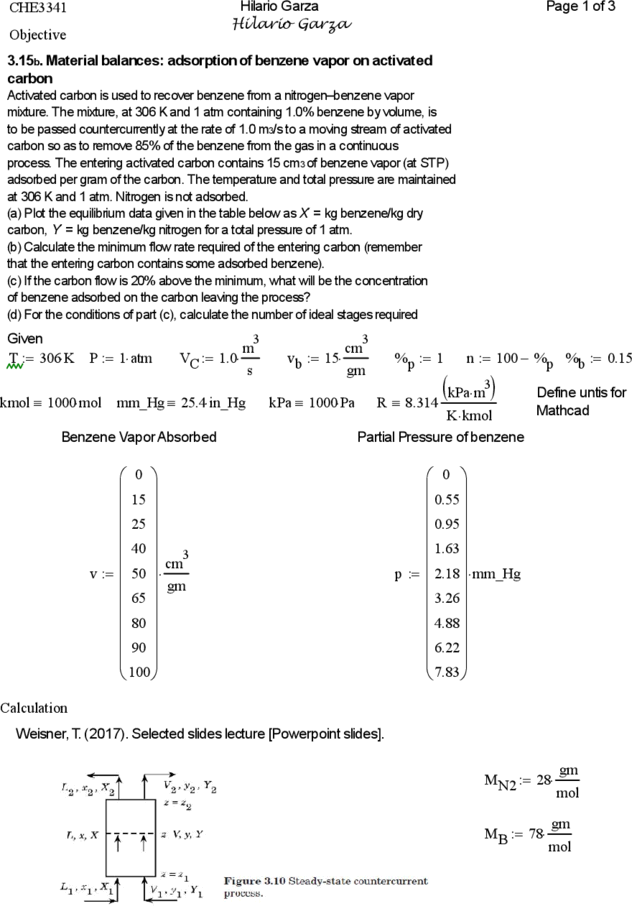
CHE3341 Hilario Garza Page 1 of 3
Hilario Garza
Objective
3.15b. Material balances: adsorption of benzene vapor on activated
carbon
Activated carbon is used to recover benzene from a nitrogen–benzene vapor
mixture. The mixture, at 306 K and 1 atm containing 1.0% benzene by volume, is
to be passed countercurrently at the rate of 1.0 m3/s to a moving stream of activated
carbon so as to remove 85% of the benzene from the gas in a continuous
process. The entering activated carbon contains 15 cm3 of benzene vapor (at STP)
adsorbed per gram of the carbon. The temperature and total pressure are maintained
at 306 K and 1 atm. Nitrogen is not adsorbed.
(a) Plot the equilibrium data given in the table below as X´ = kg benzene/kg dry
carbon, Y´ = kg benzene/kg nitrogen for a total pressure of 1 atm.
(b) Calculate the minimum flow rate required of the entering carbon (remember
that the entering carbon contains some adsorbed benzene).
(c) If the carbon flow is 20% above the minimum, what will be the concentration
of benzene adsorbed on the carbon leaving the process?
(d) For the conditions of part (c), calculate the number of ideal stages required
Given 3 3
m cm
T 306 K P 1 atm VC 1.0 v b 15 %p 1 n 100 %p %b 0.15
s gm
kmol 1000 mol mm_Hg 25.4 in_Hg kPa 1000 Pa R 8.314
kPam3 Define untis for
K kmol Mathcad
Benzene Vapor Absorbed Partial Pressure of benzene
0 0
15 0.55
25 0.95
40 cm3 1.63
v 50 p 2.18 mm_Hg
65 gm 3.26
80 4.88
90 6.22
100 7.83
Calculation
Weisner, T. (2017). Selected slides lecture [Powerpoint slides].
gm
M N2 28
mol
gm
M B 78
mol
For an ideal gas, 1 mole is the same as 22.4 L or 22,400 cm^3/mol at STP
3
cm
STP 22400
mol
A)
( 1 ) X
v M B Y p MB
(2)
STP 760 mm_Hg p M N2
0
0 2.017 10 3
0.052
0.087 3.487 10 3
0.139 5.987 10 3
X 0.174 Y
3
X and Y similar equations can be
0.226 8.014 10 found in the book from example
0.012 3.8 pg 190
0.279
0.313 0.018
0.348 0.023
0.029
Plot
0.03
0.02
Y
0.01
0
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
X
CHE3341 Hilario Garza Page 2 of 3
Hilario Garza
B)
(3) Y1
%p M B Y1 0.028
n M N2
3
(4) Y2 %b Y1 Y2 4.221 10
(5) X2
v b M B X2 0.052
STP
Using Interpolation Xmax
is about .342
Xmax .342
( 1 .1) VC P MN2 kg Mass flow rate of vapor phase
(6) Vs Vs 1.004
R T s used equation from ex. 3.7
Y1 Y2 kg
(7) Ls X Vs Ls 0.083 Mass flow rate of liquid phase
max X2
s rearrange equation 3-48
kg
(8)
Lsmin 1 X2 Ls Lsmin 0.087
s
Mass flow rate of liquid phase
C)
kg mass flow rate
La 1.2 Ls La 0.099
s
Y1 Y2
X1 X2 Vs X1 0.294 Equation from example 3.7
D) La concentation leaving absorber
From Disscusion on 2/22 the number of stages is 3
CHE3341 Hilario Garza Page 2 of 3
Hilario Garza
Aussme A=1
( 0.295 .277)
N 3 N 3.31
0.335 .277
Resuls:
A)
0.03
0.02
Y
0.01
0
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
X
B)
kg
Lsmin 0.087
s
C)
X1 0.294
D)
N 3.31
Referance:
Weisner, T. (2017) CHE 3341 Disscusion Board. TTU website
https://ttu.blackboard.com/webapps/discussionboard/do/forum?action=list_threads&course_id=_50
317_1&nav=discussion_board_entry&conf_id=_104686_1&forum_id=_178711_1
Benitez, J. (2017). Principles and modern applications of mass transfer operations. 3rd ed.
Hoboken,New Jersey,
Uriel de Jesus Garza (2017) Disscuision on problem 3.16. Lubbock, Tx. Lecture.
Pritchard , P (2008). Mathcad a tool for engineering problem solving. 2nd ed. New york,New York
CHE3341 Hilario Garza Page 1 of 2
Hilario Garza
Objective
3.16b. Material balances: desorption of benzene vapor from
activated carbon
The activated carbon leaving the adsorber of Problem 3.15 is regenerated
by countercurrent contact with steam at 380 K and 1 atm. The regenerated
carbon is returned to the adsorber, while the mixtur...
Hilario Garza
Objective
3.15b. Material balances: adsorption of benzene vapor on activated
carbon
Activated carbon is used to recover benzene from a nitrogen–benzene vapor
mixture. The mixture, at 306 K and 1 atm containing 1.0% benzene by volume, is
to be passed countercurrently at the rate of 1.0 m3/s to a moving stream of activated
carbon so as to remove 85% of the benzene from the gas in a continuous
process. The entering activated carbon contains 15 cm3 of benzene vapor (at STP)
adsorbed per gram of the carbon. The temperature and total pressure are maintained
at 306 K and 1 atm. Nitrogen is not adsorbed.
(a) Plot the equilibrium data given in the table below as X´ = kg benzene/kg dry
carbon, Y´ = kg benzene/kg nitrogen for a total pressure of 1 atm.
(b) Calculate the minimum flow rate required of the entering carbon (remember
that the entering carbon contains some adsorbed benzene).
(c) If the carbon flow is 20% above the minimum, what will be the concentration
of benzene adsorbed on the carbon leaving the process?
(d) For the conditions of part (c), calculate the number of ideal stages required
Given 3 3
m cm
T 306 K P 1 atm VC 1.0 v b 15 %p 1 n 100 %p %b 0.15
s gm
kmol 1000 mol mm_Hg 25.4 in_Hg kPa 1000 Pa R 8.314
kPam3 Define untis for
K kmol Mathcad
Benzene Vapor Absorbed Partial Pressure of benzene
0 0
15 0.55
25 0.95
40 cm3 1.63
v 50 p 2.18 mm_Hg
65 gm 3.26
80 4.88
90 6.22
100 7.83
Calculation
Weisner, T. (2017). Selected slides lecture [Powerpoint slides].
gm
M N2 28
mol
gm
M B 78
mol
For an ideal gas, 1 mole is the same as 22.4 L or 22,400 cm^3/mol at STP
3
cm
STP 22400
mol
A)
( 1 ) X
v M B Y p MB
(2)
STP 760 mm_Hg p M N2
0
0 2.017 10 3
0.052
0.087 3.487 10 3
0.139 5.987 10 3
X 0.174 Y
3
X and Y similar equations can be
0.226 8.014 10 found in the book from example
0.012 3.8 pg 190
0.279
0.313 0.018
0.348 0.023
0.029
Plot
0.03
0.02
Y
0.01
0
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
X
CHE3341 Hilario Garza Page 2 of 3
Hilario Garza
B)
(3) Y1
%p M B Y1 0.028
n M N2
3
(4) Y2 %b Y1 Y2 4.221 10
(5) X2
v b M B X2 0.052
STP
Using Interpolation Xmax
is about .342
Xmax .342
( 1 .1) VC P MN2 kg Mass flow rate of vapor phase
(6) Vs Vs 1.004
R T s used equation from ex. 3.7
Y1 Y2 kg
(7) Ls X Vs Ls 0.083 Mass flow rate of liquid phase
max X2
s rearrange equation 3-48
kg
(8)
Lsmin 1 X2 Ls Lsmin 0.087
s
Mass flow rate of liquid phase
C)
kg mass flow rate
La 1.2 Ls La 0.099
s
Y1 Y2
X1 X2 Vs X1 0.294 Equation from example 3.7
D) La concentation leaving absorber
From Disscusion on 2/22 the number of stages is 3
CHE3341 Hilario Garza Page 2 of 3
Hilario Garza
Aussme A=1
( 0.295 .277)
N 3 N 3.31
0.335 .277
Resuls:
A)
0.03
0.02
Y
0.01
0
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4
X
B)
kg
Lsmin 0.087
s
C)
X1 0.294
D)
N 3.31
Referance:
Weisner, T. (2017) CHE 3341 Disscusion Board. TTU website
https://ttu.blackboard.com/webapps/discussionboard/do/forum?action=list_threads&course_id=_50
317_1&nav=discussion_board_entry&conf_id=_104686_1&forum_id=_178711_1
Benitez, J. (2017). Principles and modern applications of mass transfer operations. 3rd ed.
Hoboken,New Jersey,
Uriel de Jesus Garza (2017) Disscuision on problem 3.16. Lubbock, Tx. Lecture.
Pritchard , P (2008). Mathcad a tool for engineering problem solving. 2nd ed. New york,New York
CHE3341 Hilario Garza Page 1 of 2
Hilario Garza
Objective
3.16b. Material balances: desorption of benzene vapor from
activated carbon
The activated carbon leaving the adsorber of Problem 3.15 is regenerated
by countercurrent contact with steam at 380 K and 1 atm. The regenerated
carbon is returned to the adsorber, while the mixtur...