Assignment
DownloadTélécharger
Actions
Vote :
ScreenshotAperçu
Informations
Catégorie :Category: mViewer GX Creator Prog HP-Prime
Auteur Author: looseygoosey
Type : Basic
Page(s) : 23
Taille Size: 2.88 Mo MB
Mis en ligne Uploaded: 23/04/2015 - 21:20:55
Uploadeur Uploader: looseygoosey (Profil)
Téléchargements Downloads: 346
Visibilité Visibility: Archive publique
Shortlink : http://ti-pla.net/a200067
Type : Basic
Page(s) : 23
Taille Size: 2.88 Mo MB
Mis en ligne Uploaded: 23/04/2015 - 21:20:55
Uploadeur Uploader: looseygoosey (Profil)
Téléchargements Downloads: 346
Visibilité Visibility: Archive publique
Shortlink : http://ti-pla.net/a200067
Description
The University of British Columbia (Okanagan Campus)
Faculty of Applied Science
School of Engineering
ENGR 305: Engineering Economic Analysis
Term 2 (2014/15)
Assignment 1
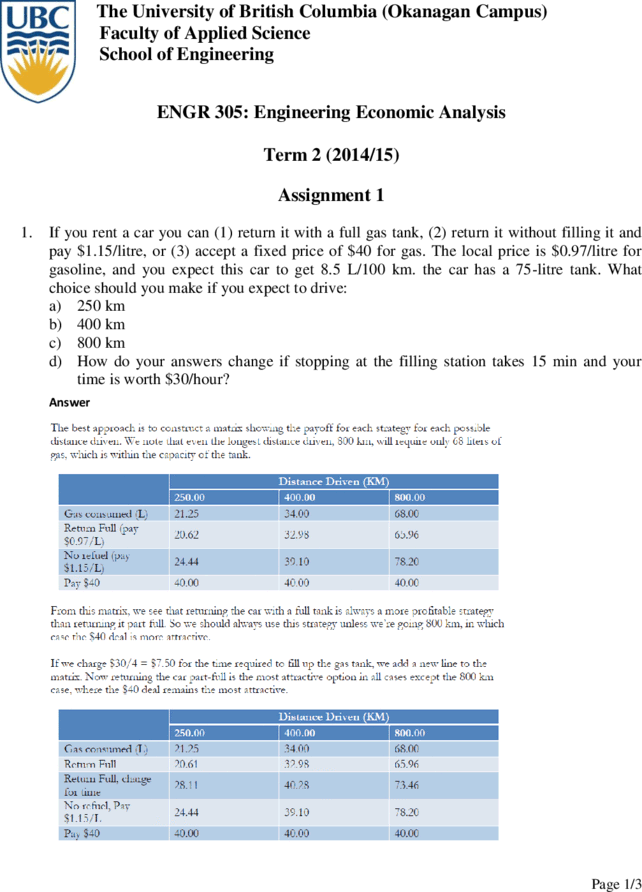
1. If you rent a car you can (1) return it with a full gas tank, (2) return it without filling it and
pay $1.15/litre, or (3) accept a fixed price of $40 for gas. The local price is $0.97/litre for
gasoline, and you expect this car to get 8.5 L/100 km. the car has a 75-litre tank. What
choice should you make if you expect to drive:
a) 250 km
b) 400 km
c) 800 km
d) How do your answers change if stopping at the filling station takes 15 min and your
time is worth $30/hour?
Answer
Page 1/3
2. A small company manufactures a certain product. Variable costs are $20 per unit and fixed
costs are $10,875. The price-demand relationship for this product is P= -0.25D + 250, where
P is the unit sales price of the product and D is the annual demand. Given that Revenue=
Demand × Price:
a) Develop the equations for total cost and total revenue
b) Find the break-even quantity for the product
c) What profit would the company obtain by maximizing its total revenue
d) What is the company’s maximum possible profit
e) Graph neatly the solutions to parts (a), (b), (c), and (d)
Answer
Page 2/3
3. Bonka Toys is considering a robot that will cost $20,000. After seven years its salvage value
will be $2,000. An overhaul costing $5,000 will be needed in year 4. Operation and
Maintenance (O&M) costs will be $2,500 per year. Draw the cash flow diagram (use
Microsoft Excel).
Answer
4. A student bought a $75 used guitar and agreed to pay for it with a single $85 payment at the
end of 6 months. Assuming semi-annual (every six months) compounding, what is the
nominal interest rate? What is the effective interest rate per year?
Answer
5. How long will it take for $10,000, invested at 5% a year, compounded continuously, to triple
in value?
Answer
Due: Thursday, February 5th, 2015 at 12:00 pm in the course drop-box.
Good Luck!
Page 3/3
The University of British Columbia (Okanagan Campus)
Faculty of Applied Science
School of Engineering
ENGR 305: Engineering Economic Analysis
Term 2 (2014/15)
Assignment 2
1. A company expects to install smog control equipment on the exhaust of a gasoline engine.
The local smog control district has agreed to pay the firm a lump sum of money to provide
for the first cost of the equipment and maintenance during its 10-year useful life. At the end
of 10 years the equipment, which initially cost $10,000, is valueless. The company and smog
control district have agreed that the following are reasonable estimates of the end-of-year
maintenance costs:
Year Maintenance Cost ($) Year Maintenance Cost ($)
1 500 6 200
2 100 7 225
3 125 8 250
4 150 9 275
5 175 10 300
Assuming interest at 6% a year, how much should the smog control district pay to the
company now to provide for the first cost of the equipment and its maintenance for 10
years?
Answer
Page 1/4
2. A student has been using his credit card too much. His plan is to use only cash until the
balance of $8,574 is paid off. The credit card company charges 18% interest, compounded
monthly.
a. What is the effective interest rate?
b. How much interest will he owe in the first month’s payment?
c. If he makes monthly payments of $225, how long will it be until it is paid off?
Answer
3. A contractor wishes to set up a special fund by making uniform semi-annual end-of-period
deposits for 20 years. The fund is to provide $10,000 at the end of each of the last five years
of the 20-year period. If interest is 8%, compounded semi-annually, what semi-annual
deposit is required?
Answer
Page 2/4
4. The local botanical society wants to ensure that the gardens in the town park are properly
cared for. They recently spent $100,000 to plant the gardens. They would like to set up a
perpetual fund to provide $100,000 for future replanting of the gardens every 10 years. If
interest is 5%, how much money would be needed to pay the cost of replanting forever?
Answer
5. The following costs are associated with three tomato-peeling machines being considered for
use in a canning plant. If the interest rate is 12%, which is the best alternative? Use NPW to
make your decision.
Machine A Machine B Machine C
Initial cost ($) $52,000 63,000 67,000
Annual maintenance 15,000 9,000 12,000
and operating costs ($)
Annual benefit ($) 38,000 31,000 37,000
Salvage value ($) 13,000 19,000 22,000
Useful life (years) 4 6 12
Page 3/4
Answer
6. A corporate bond has a face value of $1,000 with its maturity date 20 years from today. The
bond pays interest semi-annually at a rate of 8% a year based on the face value. The interest
rate paid on similar corporate bonds has decreased to a current rate of 6%. Determine the
market value of the bond.
Answer
Due: Thursday, February 19th, 2015 at 12:00 pm in the course drop-box.
Good Luck!
Page 4/4
The University of British Columbia (Okanagan Campus)
Faculty of Applied Science
School of Engineering
ENGR 305: Engineering Economic Analysis
Term 2 (2014/15)
Assignment 3
1. Amanda and Blake have found a house, which because of a depressed real estate market
costs only $201,500. They will put $22,000 down and finance the remainder with a 30-year
mortgage loan from the bank at 4.65% interest.
a) How much is their monthly loan payment?
b) How much interest will they pay in the second payment?
c) If they will also have the following expenses: property taxes of $2,100, homeowners’
insurance of $1,625, and $290 mortgage insurance. These annual amounts are paid in 12
instalments and added to the loan payment. What will Amanda and Blake’s full monthly
cost be?
d) If they can afford $1,200 a month, can Amanda and Blake afford this house?
Answer
Page 1/6
2. Consider the following three mutually exclusive alternatives:
A B C
Cost ($) 10,000 15,000 20,000
Uniform annual benefit ($) 1,000 1,762 5,548
Useful life, in years ∞ 20 5
Assuming that alternatives B and C are replaced with identical replacements at the end of their
useful lives, and an 8% interest rate, which alternative should be selected? Use an annual cash
flow analysis in working this problem.
Answer
3. A mining firm makes annual deposits of $250,000 into a reclamation fund for 20 years. If
the firm must have $10 million when the mine is closed, what interest rate must the
investment earn?
Answer
Page 2/6
4. Installing an automated production system costing $278,000 initially is expected to save Zia
Corporation $52,000 in expenses annually. If the system needs expenditures of $5,000 on
operations and maintenance each year and has a salvage value of $25,000 at end-of-year 10,
what is the IRR for 10 years’ use of this system? If the company wants to earn at least 12%
on all investments, should it buy this system?
Answer
5. Two alternatives are being considered:
A B
Initial Cost ($) 9,200 5,000
Uniform annual benefit ($) 1,850 1,750
Useful life, in years 8 4
Base your computations on a MARR of 7% and an eight-year analysis period. If identical
replacement is assumed, which alternative should be chosen?
Page 3/6
Answer
6. The following information refers to three mutually exclusive alternatives. The decision
maker wishes to choose the right machine but is uncertain what MARR to use. Create a
choice table that will help him make the correct economic decisions (use the graphical
approach).
Machine X Machine Y Machine Z
Initial Cost ($) 200 700 425
Uniform annual benefit ($) 65 110 100
Useful life, in years 6 12 8
Page 4/6
Page 5/6
Due: Thursday, March 26th, 2015 at 12:00 pm in the course drop-box.
Good Luck!
Page 6/6
The University of British Columbia (Okanagan Campus)
Faculty of Applied Science
School of Engineering
ENGR 305: Engineering Economic Analysis
Term 2 (2014/15)
Assignment 4
1. A company is considering buying a new bottle-capping machine. The initial cost of the
machine is $325,000, and it has a 10-year life. Monthly maintenance costs are expected to be
$1,200 a month for the first seven years and $2,000 a month for the remaining years. The
machine requires a major overhaul costing $55,000 at the end of the fifth year of service.
Assume that all these costs occur at the end of the relevant period. What is the future value
of all the costs of owning and operating this machine if the nominal interest rate is 7.2%?
Answer
Page 1/7
2. Using benefit-cost ratio analysis, a five-year useful life, and a 15% MARR, determine which
of the following alternatives should be selected.
A B C D E
Initial Cost ($) 100 200 300 400 500
Uniform annual benefit ($) 37 69 83 126 150
Answer
Page 2/7
3. Consider four mutually exclusive alternatives:
A B C D
Initial Cost ($) 75 50 15 90
Uniform annual benefit ($) 18.8 13.9 4.5 23.8
Each alternative has a five-year useful life and no salvage value. The MARR is 10%. Which
alternative should be selected if one uses:
a) Future worth analysis
b) Benefit-cost-ratio analysis
c) Payback period analysis
Answer
Page 3/7
4. Plan A requires a $100,000 investment now. Plan B requires an $80,000 investment now and
an additional $40,000 investment at a later time. At 8% interest, compute the break-even
point for the timing of the $40,000 investment.
Answer
Page 4/7
5. A project has a life of 10 years and no salvage value. The firm uses an interest rate of 12%
to evaluate engineering projects. The project has an uncertain first cost and net revenue.
First Cost ($) P Net Revenue ($) P
300,000 0.2 70,000 0.3
400,000 0.5 90,000 0.5
600,000 0.3 100,000 0.2
a) What is the joint probability distribution for first cost and net revenue?
b) Define optimistic, most likely, and pessimistic scenarios by using both optimistic, both
most likely, and both pessimistic estimates. What is the present worth for each scenario?
Answer
Page 5/7
6. The tree in the figure below has probabilities after each chance node and PW values for each
terminal node. What is the expected value? What decision should be made?
Answer
Page 6/7
7. A new machine will cost $25,000. The machine is expected to last four years and have no
salvage value. If the interest rate is 12%, determine the return and the risk associated with
the purchase.
P 0.3 0.4 0.3
Annual savings ($) 7,000 8,500 9,500
Answer
Due: Thursday, April 2nd, 2015 at 12:00 pm in the course drop-box.
Good Luck!
Page 7/7
The University of British Columbia (Okanagan Campus)
Faculty of Applied Science
School of Engineering
ENGR 305: Engineering Economic Analysis
Term 2 (2014/15)
Assignment 5
1. A depreciable asset costs $10,000 and has an estimated salvage value of $1,600 at the end of
its six-year depreciable life. Compute the depreciation schedule for this asset by both SOYD
depreciation and DDB depreciation.
Answer
2. The depreciation schedule for an asset with a salvage value of $90 at the end of the recovery
period has been computed by several methods. Identify the depreciation method used for
each schedule.
Year A B C D E
1 $323.30 $212.00 $424.00 $194.00 $212.00
2 258.70 339.20 254.40 194.00 339.20
3 194.00 203.50 152.60 194.00 203.52
4 129.30 122.10 91.60 194.00 122.11
5 64.70 122.10 47.40 194.00 73.27
6 61.10
Answer
Page 1/3
3. A man bought a 5% tax-free provincial bond. It cost $1,000 and will pay $50 interest each
year for 20 years. At maturity the bond returns the original $1,000. If there is 2% annual
inflation, what real rate of return will the investor receive?
Answer
4. Pollution control equipment must be purchased to remove the suspended organic material
from liquid being discharged from a vegetable packing plant. Two different pieces of
equipment are available that would accomplish the task. A Filterco unit costs $7,000 and has
a five-year useful life. A Duro unit, on the other hand, costs $10,000 but will have a 10-year
useful life. With inflation, equipment costs rise at 8% per year, compounded annually, so
that when the Filterco unit needed to be replaced, the cost would be much more than $7,000.
Using a 10-year analysis period and a 20% minimum attractive rate of return, calculate
which piece of pollution control equipment should be purchased.
Answer
Page 2/3
5. Homeowner Henry is building a fireplace for his house. The fireplace will require 800
bricks.
a) If the cost of a chimney brick in 1978 was $2.10, calculate the material cost of Henry’s
project in in 1998. The chimney brick index (CBI) was 442 in 1978 and is expected to be
618 in 1998.
b) Estimate the cost of materials for a similar fireplace to be built in the year 2008. What
assumption did you make?
Answer
b- Here we need f% of brick cost
CBI (1978)= 442
CBI (1998)= 618
n= 20
i*= ?
i*= (618/442)1/20 – 1= 1.69%
We assume the past average inflation rate continues for 10 more years.
Brick unit cost in 2008= 2.94 (F/P, 1.69%,10)= $3.48
Total Material Cost= 800 * 3.48= $2,784
Due: Thursday, April 9th, 2015 at 12:00 pm in the course drop-box.
Good Luck!
Page 3/3
Faculty of Applied Science
School of Engineering
ENGR 305: Engineering Economic Analysis
Term 2 (2014/15)
Assignment 1
1. If you rent a car you can (1) return it with a full gas tank, (2) return it without filling it and
pay $1.15/litre, or (3) accept a fixed price of $40 for gas. The local price is $0.97/litre for
gasoline, and you expect this car to get 8.5 L/100 km. the car has a 75-litre tank. What
choice should you make if you expect to drive:
a) 250 km
b) 400 km
c) 800 km
d) How do your answers change if stopping at the filling station takes 15 min and your
time is worth $30/hour?
Answer
Page 1/3
2. A small company manufactures a certain product. Variable costs are $20 per unit and fixed
costs are $10,875. The price-demand relationship for this product is P= -0.25D + 250, where
P is the unit sales price of the product and D is the annual demand. Given that Revenue=
Demand × Price:
a) Develop the equations for total cost and total revenue
b) Find the break-even quantity for the product
c) What profit would the company obtain by maximizing its total revenue
d) What is the company’s maximum possible profit
e) Graph neatly the solutions to parts (a), (b), (c), and (d)
Answer
Page 2/3
3. Bonka Toys is considering a robot that will cost $20,000. After seven years its salvage value
will be $2,000. An overhaul costing $5,000 will be needed in year 4. Operation and
Maintenance (O&M) costs will be $2,500 per year. Draw the cash flow diagram (use
Microsoft Excel).
Answer
4. A student bought a $75 used guitar and agreed to pay for it with a single $85 payment at the
end of 6 months. Assuming semi-annual (every six months) compounding, what is the
nominal interest rate? What is the effective interest rate per year?
Answer
5. How long will it take for $10,000, invested at 5% a year, compounded continuously, to triple
in value?
Answer
Due: Thursday, February 5th, 2015 at 12:00 pm in the course drop-box.
Good Luck!
Page 3/3
The University of British Columbia (Okanagan Campus)
Faculty of Applied Science
School of Engineering
ENGR 305: Engineering Economic Analysis
Term 2 (2014/15)
Assignment 2
1. A company expects to install smog control equipment on the exhaust of a gasoline engine.
The local smog control district has agreed to pay the firm a lump sum of money to provide
for the first cost of the equipment and maintenance during its 10-year useful life. At the end
of 10 years the equipment, which initially cost $10,000, is valueless. The company and smog
control district have agreed that the following are reasonable estimates of the end-of-year
maintenance costs:
Year Maintenance Cost ($) Year Maintenance Cost ($)
1 500 6 200
2 100 7 225
3 125 8 250
4 150 9 275
5 175 10 300
Assuming interest at 6% a year, how much should the smog control district pay to the
company now to provide for the first cost of the equipment and its maintenance for 10
years?
Answer
Page 1/4
2. A student has been using his credit card too much. His plan is to use only cash until the
balance of $8,574 is paid off. The credit card company charges 18% interest, compounded
monthly.
a. What is the effective interest rate?
b. How much interest will he owe in the first month’s payment?
c. If he makes monthly payments of $225, how long will it be until it is paid off?
Answer
3. A contractor wishes to set up a special fund by making uniform semi-annual end-of-period
deposits for 20 years. The fund is to provide $10,000 at the end of each of the last five years
of the 20-year period. If interest is 8%, compounded semi-annually, what semi-annual
deposit is required?
Answer
Page 2/4
4. The local botanical society wants to ensure that the gardens in the town park are properly
cared for. They recently spent $100,000 to plant the gardens. They would like to set up a
perpetual fund to provide $100,000 for future replanting of the gardens every 10 years. If
interest is 5%, how much money would be needed to pay the cost of replanting forever?
Answer
5. The following costs are associated with three tomato-peeling machines being considered for
use in a canning plant. If the interest rate is 12%, which is the best alternative? Use NPW to
make your decision.
Machine A Machine B Machine C
Initial cost ($) $52,000 63,000 67,000
Annual maintenance 15,000 9,000 12,000
and operating costs ($)
Annual benefit ($) 38,000 31,000 37,000
Salvage value ($) 13,000 19,000 22,000
Useful life (years) 4 6 12
Page 3/4
Answer
6. A corporate bond has a face value of $1,000 with its maturity date 20 years from today. The
bond pays interest semi-annually at a rate of 8% a year based on the face value. The interest
rate paid on similar corporate bonds has decreased to a current rate of 6%. Determine the
market value of the bond.
Answer
Due: Thursday, February 19th, 2015 at 12:00 pm in the course drop-box.
Good Luck!
Page 4/4
The University of British Columbia (Okanagan Campus)
Faculty of Applied Science
School of Engineering
ENGR 305: Engineering Economic Analysis
Term 2 (2014/15)
Assignment 3
1. Amanda and Blake have found a house, which because of a depressed real estate market
costs only $201,500. They will put $22,000 down and finance the remainder with a 30-year
mortgage loan from the bank at 4.65% interest.
a) How much is their monthly loan payment?
b) How much interest will they pay in the second payment?
c) If they will also have the following expenses: property taxes of $2,100, homeowners’
insurance of $1,625, and $290 mortgage insurance. These annual amounts are paid in 12
instalments and added to the loan payment. What will Amanda and Blake’s full monthly
cost be?
d) If they can afford $1,200 a month, can Amanda and Blake afford this house?
Answer
Page 1/6
2. Consider the following three mutually exclusive alternatives:
A B C
Cost ($) 10,000 15,000 20,000
Uniform annual benefit ($) 1,000 1,762 5,548
Useful life, in years ∞ 20 5
Assuming that alternatives B and C are replaced with identical replacements at the end of their
useful lives, and an 8% interest rate, which alternative should be selected? Use an annual cash
flow analysis in working this problem.
Answer
3. A mining firm makes annual deposits of $250,000 into a reclamation fund for 20 years. If
the firm must have $10 million when the mine is closed, what interest rate must the
investment earn?
Answer
Page 2/6
4. Installing an automated production system costing $278,000 initially is expected to save Zia
Corporation $52,000 in expenses annually. If the system needs expenditures of $5,000 on
operations and maintenance each year and has a salvage value of $25,000 at end-of-year 10,
what is the IRR for 10 years’ use of this system? If the company wants to earn at least 12%
on all investments, should it buy this system?
Answer
5. Two alternatives are being considered:
A B
Initial Cost ($) 9,200 5,000
Uniform annual benefit ($) 1,850 1,750
Useful life, in years 8 4
Base your computations on a MARR of 7% and an eight-year analysis period. If identical
replacement is assumed, which alternative should be chosen?
Page 3/6
Answer
6. The following information refers to three mutually exclusive alternatives. The decision
maker wishes to choose the right machine but is uncertain what MARR to use. Create a
choice table that will help him make the correct economic decisions (use the graphical
approach).
Machine X Machine Y Machine Z
Initial Cost ($) 200 700 425
Uniform annual benefit ($) 65 110 100
Useful life, in years 6 12 8
Page 4/6
Page 5/6
Due: Thursday, March 26th, 2015 at 12:00 pm in the course drop-box.
Good Luck!
Page 6/6
The University of British Columbia (Okanagan Campus)
Faculty of Applied Science
School of Engineering
ENGR 305: Engineering Economic Analysis
Term 2 (2014/15)
Assignment 4
1. A company is considering buying a new bottle-capping machine. The initial cost of the
machine is $325,000, and it has a 10-year life. Monthly maintenance costs are expected to be
$1,200 a month for the first seven years and $2,000 a month for the remaining years. The
machine requires a major overhaul costing $55,000 at the end of the fifth year of service.
Assume that all these costs occur at the end of the relevant period. What is the future value
of all the costs of owning and operating this machine if the nominal interest rate is 7.2%?
Answer
Page 1/7
2. Using benefit-cost ratio analysis, a five-year useful life, and a 15% MARR, determine which
of the following alternatives should be selected.
A B C D E
Initial Cost ($) 100 200 300 400 500
Uniform annual benefit ($) 37 69 83 126 150
Answer
Page 2/7
3. Consider four mutually exclusive alternatives:
A B C D
Initial Cost ($) 75 50 15 90
Uniform annual benefit ($) 18.8 13.9 4.5 23.8
Each alternative has a five-year useful life and no salvage value. The MARR is 10%. Which
alternative should be selected if one uses:
a) Future worth analysis
b) Benefit-cost-ratio analysis
c) Payback period analysis
Answer
Page 3/7
4. Plan A requires a $100,000 investment now. Plan B requires an $80,000 investment now and
an additional $40,000 investment at a later time. At 8% interest, compute the break-even
point for the timing of the $40,000 investment.
Answer
Page 4/7
5. A project has a life of 10 years and no salvage value. The firm uses an interest rate of 12%
to evaluate engineering projects. The project has an uncertain first cost and net revenue.
First Cost ($) P Net Revenue ($) P
300,000 0.2 70,000 0.3
400,000 0.5 90,000 0.5
600,000 0.3 100,000 0.2
a) What is the joint probability distribution for first cost and net revenue?
b) Define optimistic, most likely, and pessimistic scenarios by using both optimistic, both
most likely, and both pessimistic estimates. What is the present worth for each scenario?
Answer
Page 5/7
6. The tree in the figure below has probabilities after each chance node and PW values for each
terminal node. What is the expected value? What decision should be made?
Answer
Page 6/7
7. A new machine will cost $25,000. The machine is expected to last four years and have no
salvage value. If the interest rate is 12%, determine the return and the risk associated with
the purchase.
P 0.3 0.4 0.3
Annual savings ($) 7,000 8,500 9,500
Answer
Due: Thursday, April 2nd, 2015 at 12:00 pm in the course drop-box.
Good Luck!
Page 7/7
The University of British Columbia (Okanagan Campus)
Faculty of Applied Science
School of Engineering
ENGR 305: Engineering Economic Analysis
Term 2 (2014/15)
Assignment 5
1. A depreciable asset costs $10,000 and has an estimated salvage value of $1,600 at the end of
its six-year depreciable life. Compute the depreciation schedule for this asset by both SOYD
depreciation and DDB depreciation.
Answer
2. The depreciation schedule for an asset with a salvage value of $90 at the end of the recovery
period has been computed by several methods. Identify the depreciation method used for
each schedule.
Year A B C D E
1 $323.30 $212.00 $424.00 $194.00 $212.00
2 258.70 339.20 254.40 194.00 339.20
3 194.00 203.50 152.60 194.00 203.52
4 129.30 122.10 91.60 194.00 122.11
5 64.70 122.10 47.40 194.00 73.27
6 61.10
Answer
Page 1/3
3. A man bought a 5% tax-free provincial bond. It cost $1,000 and will pay $50 interest each
year for 20 years. At maturity the bond returns the original $1,000. If there is 2% annual
inflation, what real rate of return will the investor receive?
Answer
4. Pollution control equipment must be purchased to remove the suspended organic material
from liquid being discharged from a vegetable packing plant. Two different pieces of
equipment are available that would accomplish the task. A Filterco unit costs $7,000 and has
a five-year useful life. A Duro unit, on the other hand, costs $10,000 but will have a 10-year
useful life. With inflation, equipment costs rise at 8% per year, compounded annually, so
that when the Filterco unit needed to be replaced, the cost would be much more than $7,000.
Using a 10-year analysis period and a 20% minimum attractive rate of return, calculate
which piece of pollution control equipment should be purchased.
Answer
Page 2/3
5. Homeowner Henry is building a fireplace for his house. The fireplace will require 800
bricks.
a) If the cost of a chimney brick in 1978 was $2.10, calculate the material cost of Henry’s
project in in 1998. The chimney brick index (CBI) was 442 in 1978 and is expected to be
618 in 1998.
b) Estimate the cost of materials for a similar fireplace to be built in the year 2008. What
assumption did you make?
Answer
b- Here we need f% of brick cost
CBI (1978)= 442
CBI (1998)= 618
n= 20
i*= ?
i*= (618/442)1/20 – 1= 1.69%
We assume the past average inflation rate continues for 10 more years.
Brick unit cost in 2008= 2.94 (F/P, 1.69%,10)= $3.48
Total Material Cost= 800 * 3.48= $2,784
Due: Thursday, April 9th, 2015 at 12:00 pm in the course drop-box.
Good Luck!
Page 3/3